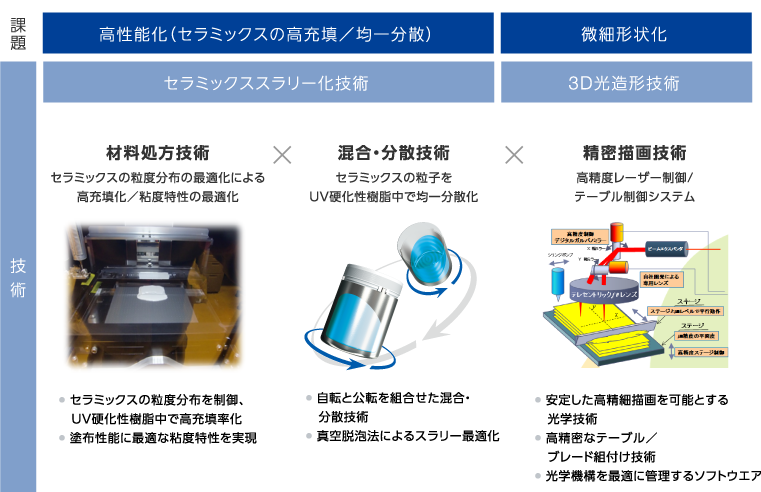
SK Fine’s Technology
Stereolithography (slurry molding) method
Our 3D stereolithography technology and ceramic slurrying technology provide complex structures that could not be made by conventional methods.
3D printer systems
| System | Stereolithography method | Material extrusion method | Laser sintering method | Binder jetting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Principle | Ultraviolet laser | Heater | CO2 laser, electron beam | Ultraviolet lamp |
| UV curing resin | Thermoplastic resin | Heat sintering | Jetting of UV curing resin | |
| Material and feed | Solution, slurry Liquid tank, blade application |
Filament nozzle | Powder Recoater roller |
Powder Recoater roller |
| Sintering | After 3D printing | After 3D printing | Direct sintering | After 3D printing |
| Size | Large △, Small ◎ | ー | ー | ー |
| Roughness | Surface ◎, Side 〇 | ー | ー | ー |
Features
Comparison between 3D printer and conventional methods
| 3D printer *Ceramic 3D stereolithography method |
Conventional methods | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sheet lamination method | Extrusion molding method | Injection molding method | ||
| Plate, mold, etc. | Not required | Required: Laminated frame, press die | Required: Mold form (plate) | Required: Mold |
| Binder | UV resin | PVA、PVB | Special-purpose resin | Thermoplastic resin |
| Dimensional accuracy | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | ◎ |
| Complex shapes | ◎ | ー | ー | ー |
| Degree of freedom in shape and structure | ◎ | Simple shapes, laminated shapes | Same cross-section, inclined structures | ◎ Mold preparation |
| Surface condition | ◎ Surface △ Laminated layer height differences | ー | ー | ー |
| Productivity | △〇 | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ |
| High-mix low volume | ◎ | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| Main products | Electronic parts, medical equipment, heat dissipation, cosmic energy, and environment system parts | Ceramic capacitors, LTCC, optical communication parts | Ceramic filters, ferrules (optical part) | Ferrules (optical part), mechanical parts, dentistry related |
Ceramic 3D printing process
-
1 Material preparation Prepare ceramic powder and UV curing resin
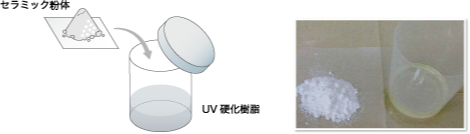
-
2 Material creation (agitation process) Use a planetary centrifugal mixer to mix the ceramic powder and UV curing resin into a slurry mixture (paste), and then set the mixture in the 3D printer.
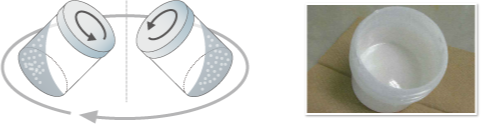
-
3 Creation of slice data for 3D printing Use slicer software to convert 3D CAD data into slice data, and enter it into the 3D printer.

-
4 Creation of 3D printed object (3D printing process) Apply the slurry material on each layer using the 3D printer, and irradiate it with a UV laser to create a 3D printed object.

-
5 Creation of 3D printed object (cleaning process) Remove uncured slurry and take out and clean the 3D printed object.

-
6 Sintering (degreasing process) Put the 3D printed object into the degreasing furnace to remove resin components.

-
7 Sintering (sintering process) Put the 3D printed object into the sintering furnace.

-
8 Completion The 3D printed object is completed when it returns to normal temperature after sintering.

